

If your browser asks for the same file again it will send the ETag with the request. The ETag is a short ID that uniquely identifies a specific version of a specific file. When a web server sends you a web page, an image or any other kind of file, it sometimes sends a text string called an entity tag (ETag) with it. LSOs are sometimes referred to as Flash cookies or super cookies.īecause LSOs are stored by your Flash player and not your browser they can be used to track all the web activity originating from one computer, not just from one browser. The most recent version of HTML, version 5, has a feature variously called web storage, DOM storage or local storage that allows websites to create small but significant databases on users’ machines.Īdobe’s Flash player has a similar feature that allows Flash content embedded in web pages to create and read locally shared objects (LSOs). ‘Super’ cookiesĪlthough cookies are the most well known way to track somebody, there are other technologies that can be used for the same ends. That’s how advertisers and tracking companies work, it’s how the same adverts can appear to follow you around the web and it’s how, for example, Twitter knows what websites you’ve visited.
#Firefox cookies location mac code
The code that creates and reads the tracking cookie is hosted by the third party and it can keep reading its own cookies as you hop from site to site. In order to track an individual from one website to another, the different sites all have to share some code from a third party website. Third party cookiesĪ website can only read the cookies that it has created – it cannot read cookies created by other sites.
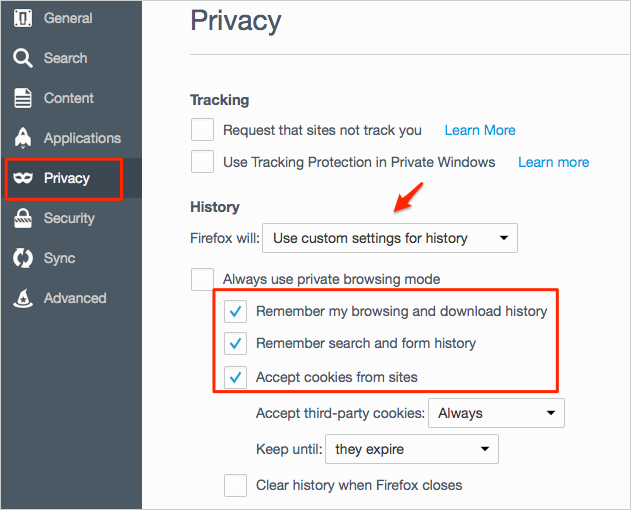
Of course, if anyone wants to track you, being able to identify two or more actions as coming from the same source is also the fundamental thing. Without this, short-term memory websites would just be brochures – there would be no Facebook, Twitter, Pinterest, LinkedIn, Amazon, eBay, Wikipedia, PayPal, WordPress, Gmail… If all your page requests contain the same unique cookie the website can see that they’re all coming from the same source.īeing able to link individual, stateless actions together like this is a fundamental building block of the web. However, if the website gives you a unique cookie the first time you ask for a page, you’ll give it back every time you ask for another page. Simplistically, a basic website will behave as if it’s the first time you’ve ever been there every single time you ask it for a web page. The HTTP protocol – the language used by web browsers to talk to websites – is stateless and no information is retained between any two HTTP events. Your browser will store the cookies until they expire and will include them in any messages it sends to the website they originally came from.Ĭookies are a normal and extremely important part of the way the web operates because they enable a sort of short-term memory. Why cookies are importantĬookies are very small pieces of information given to your web browser by the sites you visit. If you already know what cookies are all about then you can skip the next bit and go straight to the instructions.
#Firefox cookies location mac how to
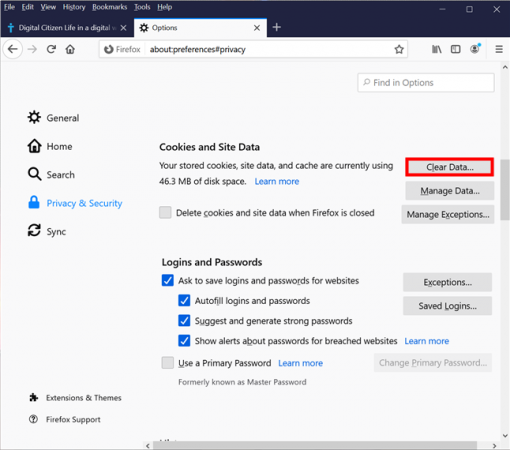
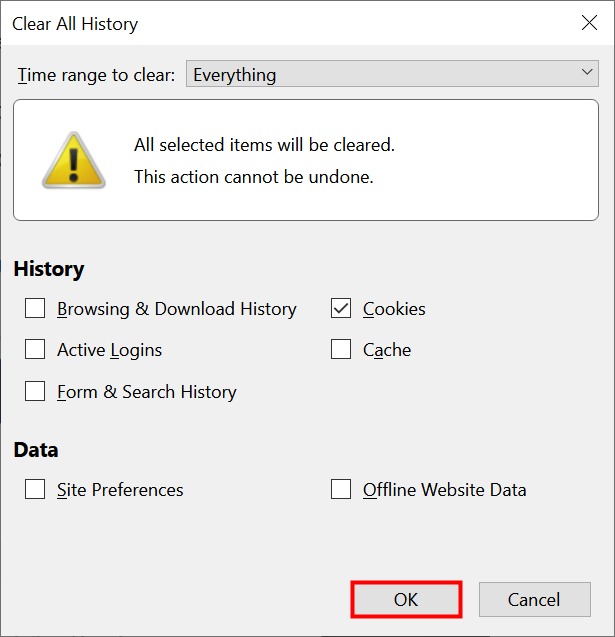
This quick fix will show you how to clear out cookies and the cookie-like things that can be used to track you online.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
